02 June 2021 – On May 31st, NYK Line, Nihon Shipyard Co. Ltd. (Nihon Shipyard), and Nippon Kaiji Kyokai (ClassNK) signed an MOU with Yara International* (Yara), Yara is a world leader in ammonia, with long experience and leading positions within global ammonia production, logistics and trade, to jointly study the practical application of an ammonia-fueled ammonia gas carrier (AFAGC) that uses ammonia as its main fuel.
Background
Since carbon dioxide (CO2) is not emitted when ammonia is burned, it is viewed to have promise as a next-generation fuel that could mitigate shipping’s impact on global warming. In addition, it is said that zero emissions can be realized by utilizing CO2-free hydrogen** as a raw material for ammonia.
In particular, the use of ammonia as a fuel for power generation is expected to significantly reduce CO2 emissions, and development is underway for ammonia co-firing power generation at coal-fired power stations.
The reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is a significant issue in the marine transportation sector. In 2018, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) set the goal of halving GHG emissions from the international maritime sector by 2050 and reaching a target of zero as early as the end of this century.
Ammonia is attracting attention from various quarters as an alternative fuel that can contribute to achieving these goals.
Overview of joint study
This project is part of joint R&D for the practical application of the world’s first AFAGC, which NYK Line, Nihon Shipyard, and ClassNK have been operating since August 2020.
AFAGC contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions from ships by using ammonia as the main fuel and is expected to achieve zero emissions from ocean-going ships at an early stage by using ammonia as a marine fuel. It will also contribute to the establishment of a stable and economical supply chain for ammonia, for which demand is expected to grow in the future.
With the signing of this MOU with Yara, we will now proceed with studies based on more specific operational requirements, including ship design and development, by studying operational methods and regulatory compliance, and evaluating economic efficiency.
Role of each company
| Yara (Charterer) | Formulation of operation requirements Evaluation of economic efficiency as a charterer |
| NYK Line (Shipowner) | Formulation of operation methods Consideration of compliance with laws and regulations Evaluation of environmental friendliness of AFAGC introduction Assessment of the economics of being a shipowner |
| Nihon Shipyard (Shipbuilding company) |
R&D and design of AFAGC Estimation of CO2 emission reductions |
| ClassNK (Classification Society) | Technical verification for safety Formulation of guidelines |
Future Outlook
Through this joint R&D, we will promote the use of ammonia as a marine fuel and aim to provide a stable supply to meet existing demand (including chemical products and raw materials for fertilizers) and new demand (including fuel use in domestic thermal power plants), which is expected to grow in the future. By doing so, the project is expected to make a significant contribution to the decarbonization of not only the maritime industry but also the energy industry.
We also aim to establish international standards as soon as possible by being actively involved in R&D in the field of safety.
* Yara International
Yara is a world leader in the production of nitrogen fertilizer The Oslo-based company produces roughly 8.5 million tonnes of ammonia annually. Yara employs a fleet of 11 ammonia carriers, including 5 fully owned ships, and owns 18 marine ammonia terminals with 580 kt of storage capacity – enabling it to produce and deliver ammonia across the globe. In February, the company established the Yara Clean Ammonia Unit, which aims to achieve a low-carbon future through clean ammonia throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to marine transportation.
Website: https://www.yara.com
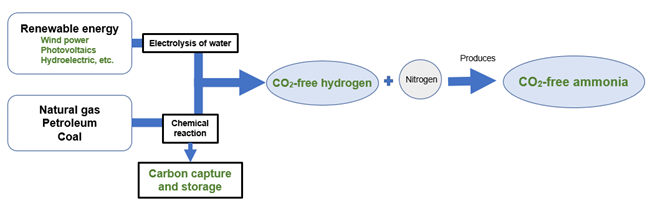
** CO2-free hydrogen
One way of producing hydrogen without generating CO2 is through the use of renewable energy. A second way is by using natural gas or coal together with carbon capture and storage. CO2-free ammonia synthesis is technology for synthesizing ammonia using such CO2-free hydrogen.
For more information on this topic please contact:
ClassNK Public Relations Team
Tel: +81-3-5226-2047
E-mail: eod@classnk.or.jp
